A thermometer is an invaluable tool in medical clinics and scientific research. It allows doctors to assess their patients’ body temperature with high accuracy, aiding in prognosis, diagnosis, and treatment.
In laboratories, thermometers help researchers maintain the right lab temperature to ensure different experiments or lab equipment do not get affected. This way, these types of thermometers play a vital role in the healthcare and the research and development sectors.
But what makes a clinical thermometer different from a laboratory thermometer? This blog covers both types of thermometers in detail to help you understand what makes them unique, so keep reading until the end.
- What is a Clinical Thermometer?
- Features of Clinical Thermometer
- How Does it Work?
- Uses of Clinical Thermometer
- What is a Laboratory Thermometer?
- Features of Laboratory Thermometer
- Uses of Laboratory Thermometer
- Differences Between Clinical Thermometer & Laboratory Thermometer
What is a Clinical Thermometer?
A clinical thermometer, sometimes also referred to as a medical or doctor’s thermometer, is a sensitive device that is used primarily to measure the human body temperature in homes, schools, clinics, and hospitals.
Traditional clinical thermometers consist of a graduated glass tube with a bulb that is filled with mercury or alcohol. Nowadays you normally see doctors using digital thermometers which use sensors or thermistors to note the temperature changes. These thermometers are more accurate as well as portable. A clinical thermometer can easily detect temperatures in the range of 95oF to 108oF.
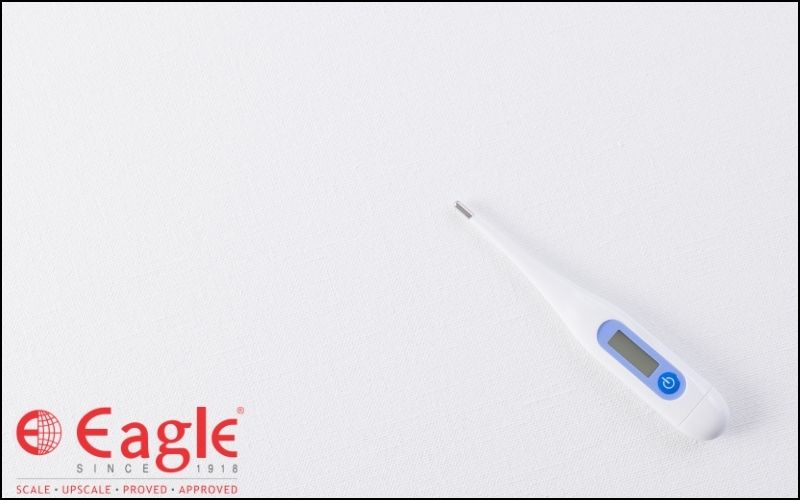

Features of Clinical Thermometer
Here are a few distinctive features of a clinical thermometer
- It has a range of about 35oC to 42oC or 95oF to 108oF.
- Its capillary comes with a Kink to stop the backflow of mercury.
- It is easy to use and requires low maintenance.
- It is made of glass and contains mercury or alcohol in the bulb.
How Does it Work?
The working of this type of thermometer is pretty straightforward. You can place it inside the mouth of the patient and the heat will cause the mercury in the bulb to melt and move into the glass tube through a thin capillary thread as its level rises.
The new mercury level gives you the body temperature. The level of mercury doesn’t change when you remove the thermometer from the mouth. This happens because there is a kink in the capillary which prevents this from happening.
To restore the mercury level, you need to jerk or swing the thermometer sharply a few times. This causes the mercury to go back allowing you to use the thermometer again after careful cleaning and sterilization.
Uses of Clinical Thermometer
The following are the main uses of clinical thermometers
- These are used in homes, clinics, and hospitals to measure body temperatures.
- These are used to monitor the health and treatment progress of patients suffering from fever or hypothermia.
- Doctors use it for diagnosis as well as treatment planning.
What is a Laboratory Thermometer?
These sophisticated thermometers are used in research labs where you have to deal with very high or very low temperatures. Typically, these thermometers can measure temperatures ranging from -10oC to 110oC.
The design of a simple laboratory thermometer is similar to a clinical thermometer except for the fact that these thermometers can measure a wide range of temperatures and they do not have a kink to stop the backflow of mercury.
These thermometers are larger in size and they have a low sensitivity but high resolution as compared to clinical thermometers.
Features of Laboratory Thermometer
Here are a few main features that set laboratory thermometers apart
- These are either made of glass or metal with alcohol or mercury in the bulb.
- Its tube is larger and thicker which gives you more readability.
- It has a very wide temperature range i.e., -10oC to 110oC.
- These thermometers are ideal for medical and material research laboratories for their high accuracy as well as durability.
Uses of Laboratory Thermometer
Following are a few applications of laboratory thermometers
- These are used in laboratories dedicated to scientific research, product development, industrial processes, etc.
- You can use these to measure the temperature of solids, liquids, as well as gases.
- These are used in the food industry to ensure the safety of edible products. They do this by allowing you to accurately measure cooking, refrigeration, and storage temperatures.
- These are used to monitor air, water, and soil temperatures for studying as well as predicting climate patterns.
Differences Between Clinical Thermometer & Laboratory Thermometer
Following are a few points of difference between clinical and laboratory thermometers:
| Clinical Thermometer | Laboratory Thermometer |
| It is used to measure body temperatures. | It is used to measure the temperature of objects as well as surroundings in a lab. |
| It has a temperature range of 35oC to 42oC. | It has a temperature range of -10oC to 110oC. |
| It has a kink to prevent the instant mercury backflow. | It doesn’t feature a kink. |
| The use of mercury in these thermometers is discouraged due to its toxicity. | You can use mercury in these thermometers without any worry. |
| These thermometers are smaller and more compact. | These thermometers are larger and broader. |
| Provides a stable reading once removed from the body and needs to be shaken down to reset before the next use. | Responds quickly to changes and provides an instantaneous reading, which can fluctuate with any temperature variation. |
| Has high precision within a narrow range (for accurate body temperature reading). | Offers precise readings over a wide temperature range, which is necessary for detailed scientific experiments. |
| Often designed with additional safety features since it comes into direct contact with people, and some use alcohol or digital technology instead of mercury. | Generally more robust to handle different chemicals and materials, but mercury is still common in some versions (or digital sensors) since it’s often not in direct contact with people. |
Conclusion
Both clinical and laboratory thermometers differ in terms of their temperature ranges as well as their intended use. Clinical thermometers are ideal for measuring body temperature that is neither extremely low nor exceptionally high.
Laboratory thermometers, on the other hand, are used in applications where you need to determine extremely higher or lower temperatures than the average human body.
So, the next time you are out buying a thermometer, it is better to consider the above points to make sure you find a product that meets your application requirements to get the best results.
Visit Eagle Scales today to order our top-quality weighing solutions both for personal as well as commercial applications.





